How to configure network on Windows Server 2012
For the correct operation of the network on Windows, regardless of whether the connection redundancy option is ordered for a server or not, it is necessary to set up link teaming (aggregate two physical interfaces into a logical one).
Servers with link aggregation have five network ports. Two ports are connected to a pair of switches in the private network, two ports are connected to a pair of switches in the public network, and one port is connected to the out-of-band (OOB) management network.
Link teaming (aka link aggregation) is configured for each pair of public and private ports. We use the LACP protocol for link aggregation. In line with our interface naming convention, "aggi" is the name of the private network aggregation interface, and "agge" is the name of the public network aggregation interface.
Setting up link aggregation
To set up teaming separately for the private network and for the public network, open Server Manager, go to the tab "Local Server" and in the "Properties" window next to the line "NIC Teaming" click "Disabled".

In the appearing window, in the "Teams" section, select "New Team" from the drop-down "Tasks" menu.

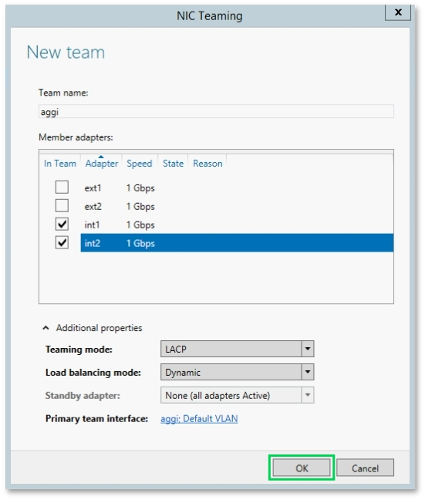
Let's set up a team for the private network first.
-
Set the name of a team to "aggi".
-
Select "int1" and "int2" network adapters as member adapters.
-
Select "LACP" in the "Teaming mode" drop-down list.
-
Leave "Load balancing mode" to "Dynamic" as it is.
-
Click "OK".
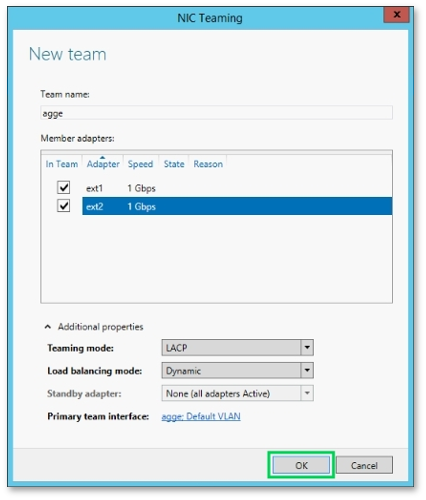
The process of setting up the public network is pretty the same, except for "Team name" which is "agge", and for "Member adapters" which are "ext1" and "ext2".
Configuring IPv4
After both teamed interfaces are created, IPv4 settings for each of them must be changed. You will need to know the private IP address of your server, the public IP address and gateways addresses which are available on the server's Details page in the Customer Portal:

To make changes to IPv4 settings, open "Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center > Change adapter settings" window. Right-click on the interface named "aggi" and select "Properties" to view network interface settings.

Select "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP / IPv4)" in the list of protocols in the appearing window and click "Properties".

Enter the following values:
-
IP address: [Private IP address of your server]
-
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.248
-
Default gateway: leave blank
-
Preferred DNS server: 192.168.8.88
-
Alternate DNS server: 192.168.8.8
-
After the data has been entered, click "OK".

Do the same procedure for the public network interface ("agge") using the following values:
-
IP address: [Public IP address of your server]
-
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.248
-
Default gateway: [Gateway IP address for the public network]
-
Preferred DNS server: Leave blank
-
Alternate DNS server: Leave blank
-
After the data has been entered, click "OK".

Adding static routes
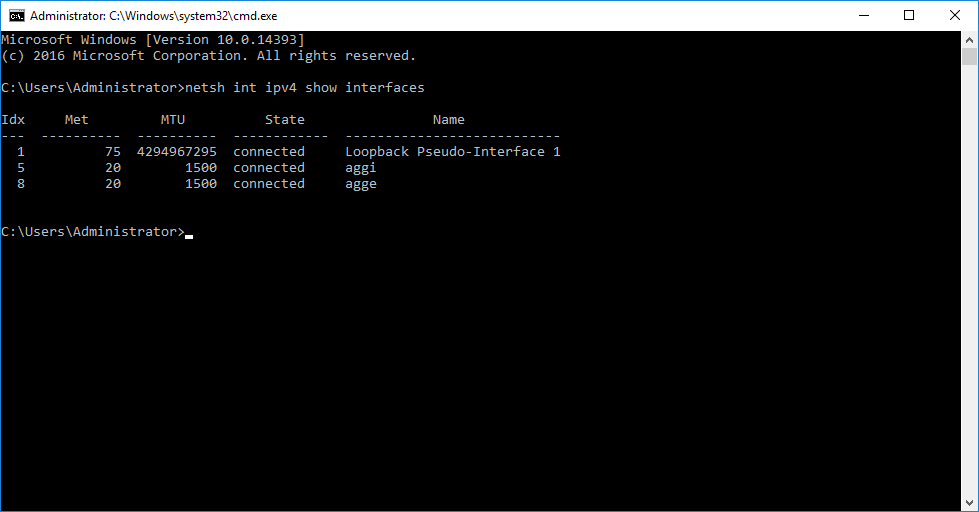
Next, for the correct operation of the network, you need to add static routes. To do this, press Ctrl + Win + R. In the appearing dialogue, type "cmd" and click "OK" to open Command Prompt. Run the following command to find out network interfaces numbers:
netsh int ipv4 show interfacesIn this sample output, you can see that "aggi" index is 5, and "agge" index is 8.
Now you need to run the following commands replacing brackets with actual data:
route -p add 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0 [Private_Gateway_IP] if [Private_Interface_ID]
route -p add 188.42.208.0 mask 255.255.248.0 [Private_Gateway_IP] if [Private_Interface_ID]
route -p add 10.0.0.0 mask 255.0.0.0 [Private_Gateway_IP] if [Private_Interface_ID]Using data from examples above, it will be:
route -p add 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0 10.148.197.76 if 5
route -p add 188.42.208.0 mask 255.255.248.0 10.148.197.76 if 5
route -p add 10.0.0.0 mask 255.0.0.0 10.148.197.76 if 5You're done!