Concepts
Dell server chassis
Dell PowerEdge servers form the backbone of our infrastructure, providing robust, high performance, resilient solutions for a wide range of computing needs.
To distinguish between the server model and chassis model, we adhere to the following terminology:
-
A chassis model is a server's body with the key components such as processors installed and the backplane, excluding attachments such as disks, RAM, and so on. The processor installed in the chassis does not change. Each chassis can accommodate several server models.
-
A server model represents a real server with all attachments (disks, RAM, additional network cards and so on).
We offer chassis with a wide range of system classes, processors, and platform generations, provisioning secure infrastructure for small businesses and providing scalability for large enterprise companies.
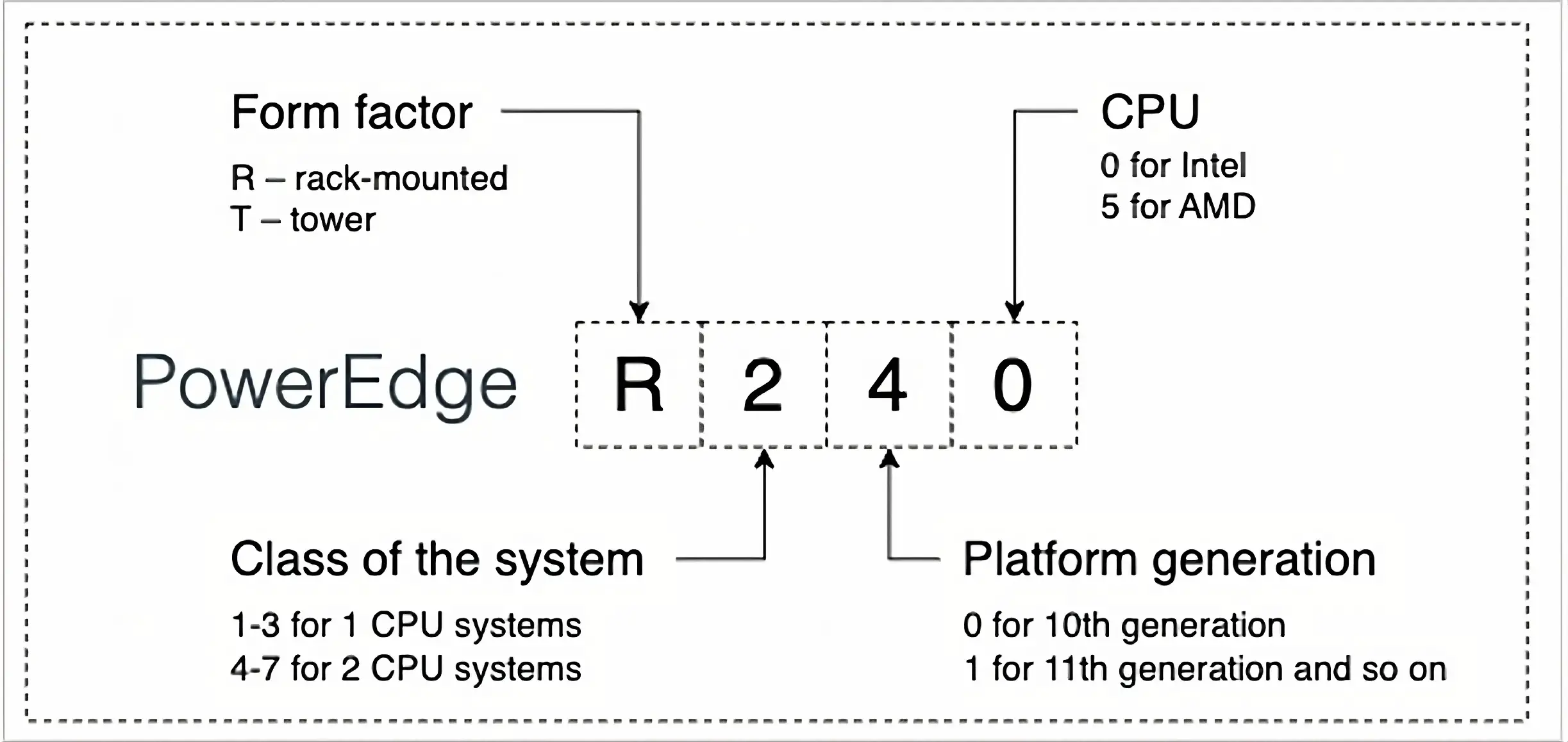
The naming convention consists of a letter followed by three numbers (e.g., PowerEdge R240):
-
1st letter is the type of chassis, known as the form factor. R is for rack-mounted, or T is for tower.
-
1st number is the class of the system: 1-3 (for 1 CPU systems) or 4-7 (for 2 CPU systems). The difference in number is their levels of performance, scalability and available features, with 3 offering more advanced specifications than 1, for example.
-
2nd number is the platform generation: starting with 0 for 10th generation, 1 means 11th generation, 2 means 12th generation, and so on.
-
3rd number is the CPU: 0 is for Intel, 5 is for AMD.
A brief description of the available server chassis:
|
Model |
Description |
|
R2xx |
R2xx servers usually do not have a RAID controller installed. The second network interface controller occupies the only PCI expansion slot. See the Network redundancy section of this article. |
|
R3xx |
Practically the same as R2xx, but it has two PSUs. |
|
R4xx |
Dual-socket 1U system. Two CPUs allows for more RAM, more PCI lanes, and so on. |
|
R5xx |
2U dual-socket system. Has more storage slots, expansion slots, and PCI lanes than R4xx. |
|
R7xx |
2U dual-socket system for storage and data processing workloads. Up to 26 x 2.5” drives per server. |
|
T6xx |
They are explicitly used for GPU servers. Despite being the "tower" type, the chassis can be installed into a server rack as a 5U unit. |
Dell servers come with an autonomous subsystem for management and monitoring capabilities – iDRAC. It is a hardware component installed on the server's motherboard and allows for server management even when the server is turned off. iDRAC provides both web and command-line interfaces.
Provisioning time
Provisioning time is the duration required to configure and provide the dedicated server in the requested configuration after it has been ordered.
Provisioning ETA:
-
40 minutes – the ordered server configuration is available in the rack
-
24 hours or more – the ordered server is not currently in the rack or configuration changes are needed
If server hardware needs to be ordered or transported, the server provisioning time is determined by the delivery deadlines.
For additional information on the server provisioning stages, refer to server provisioning.
Responsibilities (customer and servers.com)
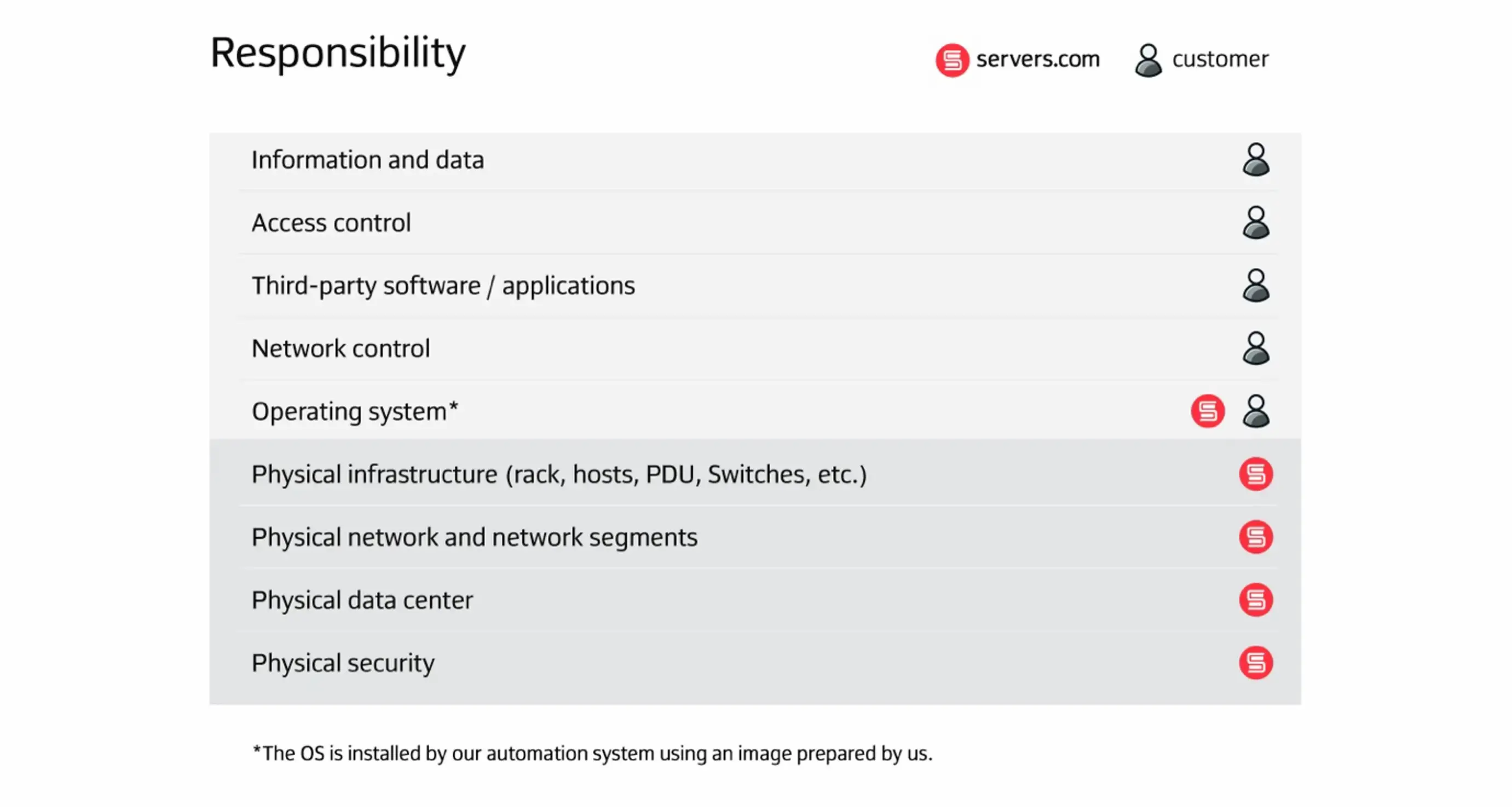
Included services
Here is what’s typically included in your order of a dedicated server:
-
Server hardware equipment
-
Internet connection
-
Connection to both a private and public network with flexible billing options
-
Public IPv4 address
-
Automated OS installation system and server booting in recovery mode
-
Out-of-band access
-
Server management environment: customer portal, public API, terraform
-
Replacement of failed components or entire server
-
24/7 technical support
How dedicated server billing works
Dedicated server billing occurs on a pre-paid basis and is proportional to the number of days the service was used within the billing period, which is one month. Invoices are automatically generated on the 1st of each month. Payment for the dedicated server and associated services is due five days from the invoice date.
The cost of the dedicated server is listed in the currency of its location and will be converted to the account currency based on the exchange rate if they differ.
What happens in case of non-payment?
If payment is not received for the issued invoice after the specified period, an overdue notice is sent to the account contacts. If the overdue notice is disregarded and payment is not received, company employees may proceed to block the ordered dedicated servers and suspend the ability to order services. This restriction does not apply to services already paid for.
Before blocking, company employees always reach out to the account manager to remind them of the outstanding balance.
Blocked dedicated servers remain assigned to the account; data is not deleted, and servers are not shut down or restarted. However, servers become inaccessible to account users via both private and public networks, as well as via the Virtual Network Computing (VNC) console.
Additional services
Here is a list of additional services that can be applied to the ordered dedicated server:
-
HDD upgrades
-
RAM upgrades
-
Paid operating systems
-
Extended traffic packages
-
Additional IP addresses
-
Uplink aggregation
We offer the possibility to discuss and fulfil custom requests for hardware and networks. These services are provided only after approval from our managers and architects.
Dedicated server ID
Each ordered dedicated server is assigned a unique identifier. This ID is used to identify the server in servers.com public API requests and for accessing technical support.
Refer to the API documentation to find out the capabilities and available operations for dedicated servers.